Android实战 – 音心播放器 (MusicActivity – 倒计时 ,进度条实现)
最后更新于:2022-04-01 10:52:56
# 1.背景
还是音乐播放界面,实现倒计时和进度条功能,基本实现过程: 当打开MusicActivity 的时候,MusicService会发送广播给MusicActivity ,后开始当前播放的时间进度,从而实现倒计时和进度条;
这里说明下 进度条是 从小到大 ,倒计时是 从大到小 ;
效果展示 :
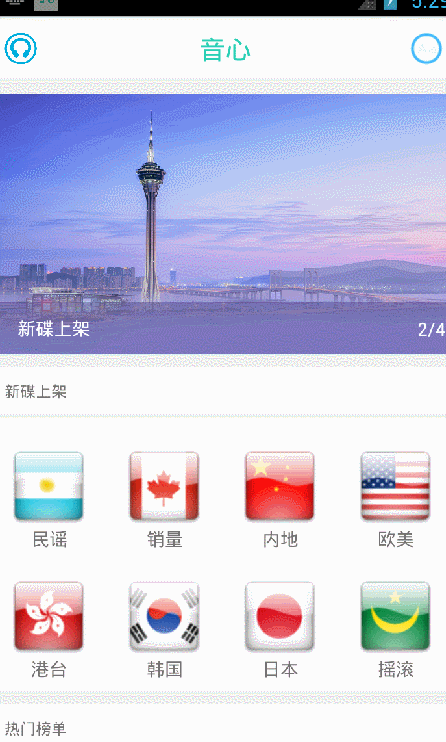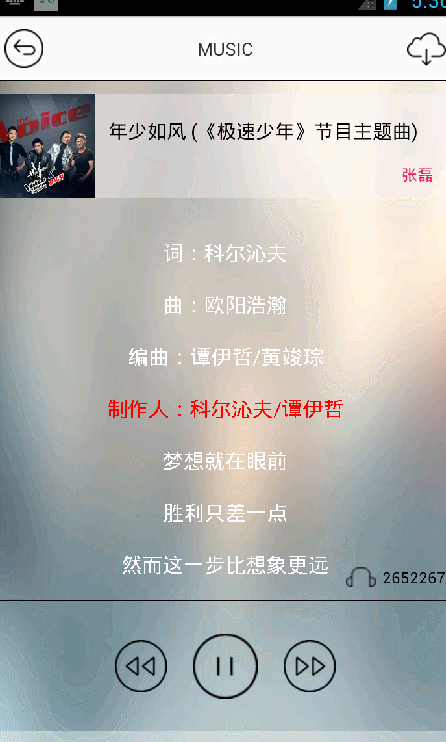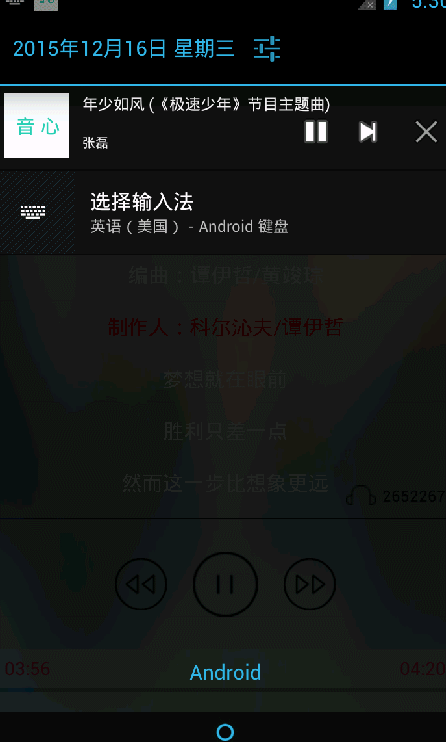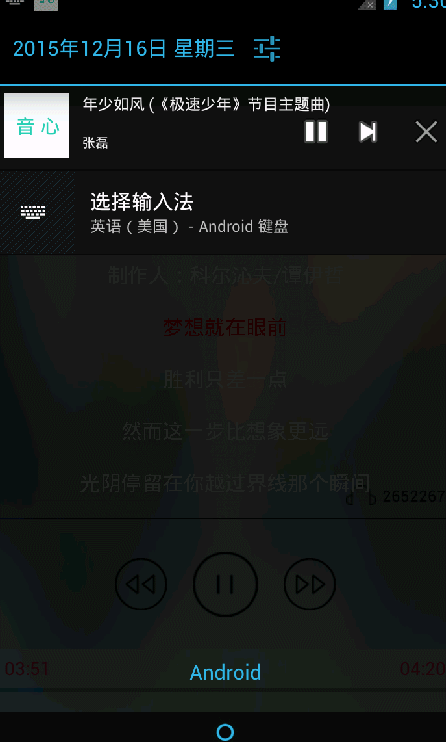
# 2.倒计时实现
实现通过CountDownTimer实现,提供了start()和cancel() 两个方法,可以开始倒计时和取消倒计时,但是,(Android5.0以下)不可以停止,这是非常不给力的;
### (1)解决方法1
在使用的时候,每次更新,将CountDownTimer 对象先调用cancel()方法,后进行销毁(赋值为null),重新创建和初始化时间,并start();
### (2)解决办法2
在网上查阅资料后,有人提供了android5.0的CountDownTimmer 源码,使用这个可以cancel(); 但是我没有成功;
源码分享:
~~~
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package cn.labelnet.ui;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.os.SystemClock;
/**
* Schedule a countdown until a time in the future, with regular notifications
* on intervals along the way.
*
* Example of showing a 30 second countdown in a text field:
*
* <pre class="prettyprint">
* new CountdownTimer(30000, 1000) {
*
* public void onTick(long millisUntilFinished) {
* mTextField.setText("seconds remaining: " + millisUntilFinished / 1000);
* }
*
* public void onFinish() {
* mTextField.setText("done!");
* }
* }.start();
* </pre>
*
* The calls to {@link #onTick(long)} are synchronized to this object so that
* one call to {@link #onTick(long)} won't ever occur before the previous
* callback is complete. This is only relevant when the implementation of
* {@link #onTick(long)} takes an amount of time to execute that is significant
* compared to the countdown interval.
*/
public abstract class CountDownTimer {
/**
* Millis since epoch when alarm should stop.
*/
private final long mMillisInFuture;
/**
* The interval in millis that the user receives callbacks
*/
private final long mCountdownInterval;
private long mStopTimeInFuture;
private boolean mCancelled = false;
/**
* @param millisInFuture
* The number of millis in the future from the call to
* {@link #start()} until the countdown is done and
* {@link #onFinish()} is called.
* @param countDownInterval
* The interval along the way to receive {@link #onTick(long)}
* callbacks.
*/
public CountDownTimer(long millisInFuture, long countDownInterval) {
mMillisInFuture = millisInFuture;
mCountdownInterval = countDownInterval;
}
/**
* Cancel the countdown.
*
* Do not call it from inside CountDownTimer threads
*/
public final void cancel() {
mHandler.removeMessages(MSG);
mCancelled = true;
}
/**
* Start the countdown.
*/
public synchronized final CountDownTimer start() {
if (mMillisInFuture <= 0) {
onFinish();
return this;
}
mStopTimeInFuture = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() + mMillisInFuture;
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG));
mCancelled = false;
return this;
}
/**
* Callback fired on regular interval.
*
* @param millisUntilFinished
* The amount of time until finished.
*/
public abstract void onTick(long millisUntilFinished);
/**
* Callback fired when the time is up.
*/
public abstract void onFinish();
private static final int MSG = 1;
// handles counting down
private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
synchronized (CountDownTimer.this) {
final long millisLeft = mStopTimeInFuture
- SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
if (millisLeft <= 0) {
onFinish();
} else if (millisLeft < mCountdownInterval) {
// no tick, just delay until done
sendMessageDelayed(obtainMessage(MSG), millisLeft);
} else {
long lastTickStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
onTick(millisLeft);
// take into account user's onTick taking time to execute
long delay = lastTickStart + mCountdownInterval
- SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
// special case: user's onTick took more than interval to
// complete, skip to next interval
while (delay < 0)
delay += mCountdownInterval;
if (!mCancelled) {
sendMessageDelayed(obtainMessage(MSG), delay);
}
}
}
}
};
}
~~~
### (3)倒计时实现
作用:
1)倒计时时间显示
2)进度条实时更新显示
3)歌词进度显示
4)播放结束 :进度条设置为0,时间设置为总时长,回调LrcView播放结束,进行歌词初始化,显示第一行。
~~~
/**
* 倒计时
*/
private class CountDownTime extends CountDownTimer {
private double second = 0;
public CountDownTime(long millisInFuture, long countDownInterval) {
super(millisInFuture, countDownInterval);
}
@Override
public void onTick(long millisUntilFinished) {
//倒计时显示操作
second = millisUntilFinished / 1000;
tv_time_sheng.setText(TimeUtil.getMinuteBySecond((int) second));
// 进度条实现更新操作
second = (allSecond - second) / allSecond * 100;
//
progressbar_music.setProgress((int) second);
// 歌词更新操作
second = allSecond * 1000 - millisUntilFinished;
// Log.d("MaskMusic", "geci : "+(long)second);
lrc.updateTime((long) second);
// lrcplaytoend.playToPause((long)
// (allSecond*1000-millisUntilFinished));
}
@Override
public void onFinish() {
// showToast("MusicActivity 播放完毕");
lrc.destroyDrawingCache();
// 播放完毕显示歌词
// showLrc();
// 播放完毕需要进行 ,初始化界面 1.进度条初始值,2.歌词回归到第一行 3.时间恢复到总时间
// 播放中 ,暂停恢复 : 1.进度条进度保持 2.歌词保持位置 3.时间保持(可以从MusicService获取)
progressbar_music.setProgress(0);
tv_time_sheng.setText(TimeUtil.getMinuteBySecond((int) allSecond));
allSecond = 0;
lrcplaytoend.playToEnd();
}
}
~~~
### (4)一个单独的方法来初始化倒计时
~~~
private void CountDown(int allTime) {
countDown = new CountDownTime(allTime, COUNT_DOWN_INTERVAL);
}
~~~
### (5)初始化倒计时所需要的判断
410001不需要看,里面的countDown是CountDownTimmer的对象,清楚该对象,重新重建倒计时,这是这里面使用的;
~~~
if (code == 41001) {
// 初始化 时间
if (countDown != null) {
countDown.cancel();
countDown = null;
}
CountDown(mm.getSeconds() * 1000);
} else {
// 销毁上一个对象
if (countDown != null) {
countDown.cancel();
countDown = null;
}
// 倒计时同步
currentTime = intent.getIntExtra(
MUSIC_SERVICE_TO_ACTIVITY_NOWTIME, 0);
CountDown(currentTime);
}
~~~
### (6)将秒转化为分
~~~
/**
* 1.秒转分
*/
public static String getMinuteBySecond(int seconds) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
int second = seconds % 60;
int minute = seconds / 60;
if (minute <= 9) {
buffer.append("0" + minute + ":");
} else {
buffer.append(minute + ":");
}
if (second <= 9) {
buffer.append("0" + second);
} else {
buffer.append(second);
}
return buffer.toString();
}
~~~
# 3.进度条实现
### (1)布局实现
直接使用的是系统的ProgressBar , 不是很漂亮但很是可以使用的;
~~~
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressbar_music"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/tv_time_sheng"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:max="100"
android:progress="50" />
~~~
### (2)控制实现
思路是倒计时在执行的时候,总时间减去当前的时间,后将时间换位百分制来使用,实时更新,如倒计时实现;
# 4.总结
倒计时和进度条的实现是相对简单的,主要是倒计时的实现,它决定了歌词显示,进度条显示,倒计时显示,三个主要的模块;在使用过程中遇到的问题就是上面的无法cancel() 。当然倒计时也可以自己去封装一个类使用,这里就不实现了。