Python for 循环语句
最后更新于:2022-03-26 23:08:32
Python for 循环语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for循环的语法格式如下:
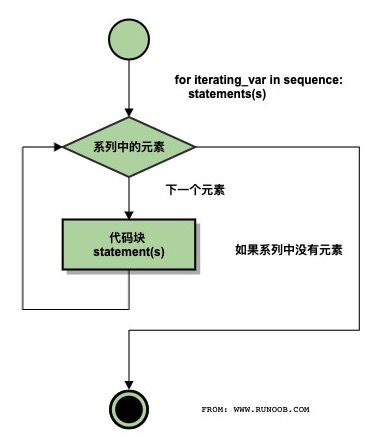
for iterating_var in sequence: statements(s)
流程图:
实例:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for letter in ‘Python‘: # 第一个实例
print("当前字母: %s" % letter) fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘]
for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例
print (‘当前水果: %s‘% fruit) print ("Good bye!")
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for letter in ‘Python‘: # 第一个实例
print("当前字母: %s" % letter) fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘]
for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例
print (‘当前水果: %s‘% fruit) print ("Good bye!")
以上实例输出结果:
当前字母: P 当前字母: y 当前字母: t 当前字母: h 当前字母: o 当前字母: n 当前水果: banana 当前水果: apple 当前水果: mango Good bye!
通过序列索引迭代
另外一种执行循环的遍历方式是通过索引,如下实例:
实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘]
for index in range(len(fruits)):
print (‘当前水果 : %s‘ % fruits[index]) print ("Good bye!")
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘]
for index in range(len(fruits)):
print (‘当前水果 : %s‘ % fruits[index]) print ("Good bye!")
以上实例输出结果:
当前水果 : banana 当前水果 : apple 当前水果 : mango Good bye!
以上实例我们使用了内置函数 len() 和 range(),函数 len() 返回列表的长度,即元素的个数。
range返回一个序列的数。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这样的意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有区别,else 中的语句会在循环正常执行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下执行,while … else 也是一样。
实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for num in range(10,20): # 迭代 10 到 20 之间的数字
for i in range(2,num): # 根据因子迭代
if num%i == 0: # 确定第一个因子
j=num/i # 计算第二个因子
print (‘%d 等于 %d * %d‘ % (num,i,j))
break # 跳出当前循环
else: # 循环的 else 部分
print (‘%d 是一个质数‘ % num)
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for num in range(10,20): # 迭代 10 到 20 之间的数字
for i in range(2,num): # 根据因子迭代
if num%i == 0: # 确定第一个因子
j=num/i # 计算第二个因子
print (‘%d 等于 %d * %d‘ % (num,i,j))
break # 跳出当前循环
else: # 循环的 else 部分
print (‘%d 是一个质数‘ % num)
以上实例输出结果:
10 等于 2 * 5 11 是一个质数 12 等于 2 * 6 13 是一个质数 14 等于 2 * 7 15 等于 3 * 5 16 等于 2 * 8 17 是一个质数 18 等于 2 * 9 19 是一个质数
更多实例:python 打印菱形、三角形、矩形