10—mysql内核调试方法
最后更新于:2022-04-01 16:04:58
在前面三篇,bingxi和alex聊了关于innodb的hash、list、以及动态数组的实现方法,这三个结构比较常用。讲完前9篇内容,本篇会描述在windows环境下debug mysql的方法,强烈建议通过debug的方式进行学习。在本篇里,bingxi和alex会聊到windows下常用的调试mysql代码的方法,仅供参考。
## 1)在windows和linux下调试的异同?
Bingxi:“alex,咱们看myslq代码的方法,是通过windows看好呢,还是linux/unix下看呢,两者之间最大的差异是什么?”
Alex:“在mysql 5.1的高版本开始,windows环境与linux环境使用同一套代码。我电脑里面正好有两个版本的代码,我们看下mysql-6.0.4-alpha目录下的INSTALL-WIN-SOURCE文件,其中有这么一段:
To build MySQL on Windows from source, you must satisfy the
following system, compiler, and resource requirements:
* Windows 2000, Windows XP, or newer version. Windows Vista is
not supported until Microsoft certifies Visual Studio 2005 on
Vista.
* CMake, which can be downloaded from http://www.cmake.org.
After installing, modify your path to include the cmake
binary.
* Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 Express Edition, Visual Studio .Net
2003 (7.1), or Visual Studio 2005 (8.0) compiler system.
* If you are using Visual C++ 2005 Express Edition, you must
also install an appropriate Platform SDK. More information and
links to downloads for various Windows platforms is available
from http://msdn.microsoft.com/platformsdk/.
* If you are compiling from a BitKeeper tree or making changes
to the parser, you need bison for Windows, which can be
downloaded from
http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/bison.htm.Download
the package labeled "Complete package, excluding sources".
After installing the package, modify your path to include the
bison binary and ensure that this binary is accessible from
Visual Studio.
* Cygwin might be necessary if you want to run the test script
or package the compiled binaries and support files into a Zip
archive. (Cygwin is needed only to test or package the
distribution, not to build it.) Cygwin is available from
http://cygwin.com.
* 3GB to 5GB of disk space.
可以通过这样的方式来生成一份代码,然后用vs2005或者更高版本来调试。
”
Bingxi:“alex,你电脑里面的另外一个软件包是mysql-5.1.7的吧。”
Alex:“嗯,这个版本是mysql5.1.7代码刚出来的时候进行下载的。这个版本的代码直接解压缩之后,可以直接用vs2003进行编译调试。对innodb而言,用这个版本的就可以了,innodb的变化不大,如果需要理解查询引擎,则需要使用更新的版本进行学习。”
Bingxi:“mysql-5.1.7-beta-win-src.zip,这个软件包的内容,我们学了之后,会不会和linux下不一样,有人会有这样的疑问,毕竟在很多公司里面,mysql是运行在linux/unix环境的。我们知道windows与linux/unix的差异还是存在的,尤其是底层的系统函数。”
Alex:“嗯,这个是很多人的疑问。其实mysql进行了代码的封装,比如在5.1.7的windows版本的代码中,也是可以看到系统函数的封装。比如event semaphore。看下对应的代码:
~~~
/*************************************************************
Creates an event semaphore, i.e., a semaphore which may just have two
states: signaled and nonsignaled. The created event is manual reset: it
must be reset explicitly by calling sync_os_reset_event. */
os_event_t
os_event_create(
/*============*/
/* out: the event handle */
const char* name) /* in: the name of the event, if NULL
the event is created without a name */
{
#ifdef __WIN__
os_event_t event;
event = ut_malloc(sizeof(struct os_event_struct));
event->handle = CreateEvent(NULL,/* No security attributes */
TRUE, /* Manual reset */
FALSE, /* Initial state nonsignaled */
(LPCTSTR) name);
if (!event->handle) {
fprintf(stderr,
"InnoDB: Could not create a Windows event semaphore; Windows error %lu/n",
(ulong) GetLastError());
}
#else /* Unix */
os_event_t event;
UT_NOT_USED(name);
event = ut_malloc(sizeof(struct os_event_struct));
os_fast_mutex_init(&(event->os_mutex));
#if defined(UNIV_HOTBACKUP) && defined(UNIV_HPUX10)
ut_a(0 == pthread_cond_init(&(event->cond_var),
pthread_condattr_default));
#else
ut_a(0 == pthread_cond_init(&(event->cond_var), NULL));
#endif
event->is_set = FALSE;
event->signal_count = 0;
#endif /* __WIN__ */
/* Put to the list of events */
os_mutex_enter(os_sync_mutex);
UT_LIST_ADD_FIRST(os_event_list, os_event_list, event);
os_event_count++;
os_mutex_exit(os_sync_mutex);
return(event);
}
~~~
在os_event_create函数体,屏蔽了系统的差异性。开发人员在开发时,需要创建event,只需要os_event_create就行了。
”
Bingxi:“alex,那么按照这个思路,是不是可以获得两个信息:1)如果需要debug系统封装函数,还是建议在linux/unix下也调试下,2)对我们查看非系统函数,在windows与linux/unix下调试,两者都是可以的。”
Alex:“嗯,用哪种调试方法都是可以的。用哪个版本的也是可以的,本系列以描述innodb存储为主,因此使用5.1.7就可以了。”
## 2)搭建windows环境下的mysql5.1.7的调试环境
Bingxi:“好吧,那我们就开始搭建环境吧。”
Alex:“ok,我们先将代码找一个目录进行解压缩,本文中的解压缩位置为d:/。使用vs2003打开D:/bin-mysql-5.1.7-beta/mysql.sln项目文件。
Bingxi,打开之后会有46个project,我们要编译其中哪些工具呢?

”
Bingxi:“ok,至少要包含下面三个内容:1)服务端程序,2)客户端程序,3)mysqladmin工具(用于退出调试时使用,直接使用中断调试太暴力了)。顺着这个思路,我们一步步来编译。
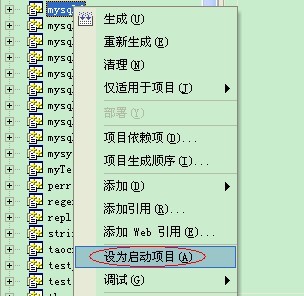
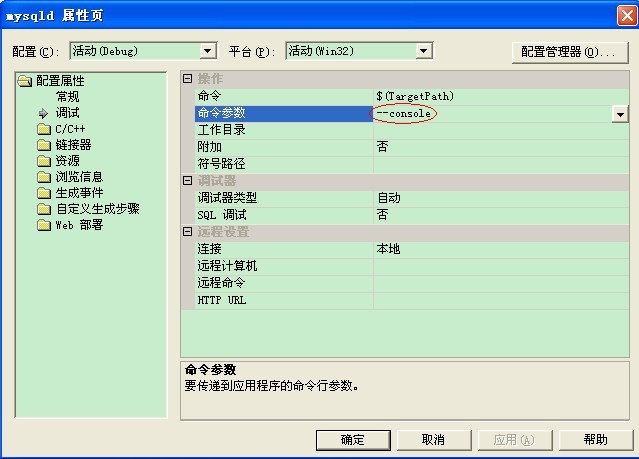
首先编译服务端程序,也就是编译mysqld项目。这里有三个建议,1)因为本系列主要调试mysqld的代码,因此需要将mysqld设置为启动项目,2)设置启动方式为console方法,这样可以在console窗口中看到打印信息,3)将D:/bin-mysql-5.1.7-beta下的data文件夹进行压缩保存,这样,我们需要恢复到原始的数据,直接用保存的data进行覆盖就可以了。
设置为启动项目:
设置为console启动方式:
根据个人习惯,决定是否将data进行压缩保存。
接着,我们编译mysqld项目、mysql项目、mysqladmin项目。编译产生的工具在D:/mysql-5.1.7-beta/client_debug目录。
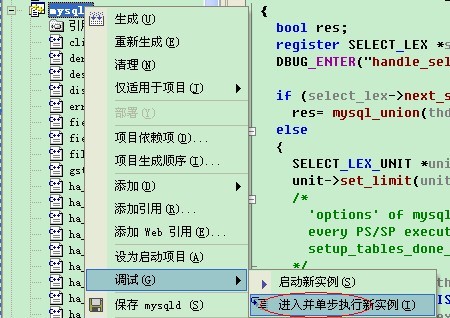
设置断点,比如查询的总入口是handle_select函数(在sql_select.cpp文件中)。使用“进入单步执行新实例”进行调试。如图:
执行时,停止在main函数开始处(可以一步步看看mysql是如何启动的),我们按F5,程序会直接执行,如果断点被执行,那么就会停在断点处,因为我们此处设置的是查询函数,所以没有被执行。因此,我们需要通过客户端执行一条语句,来触发断点对应的代码被执行。
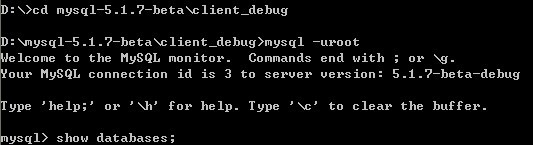
执行show databases命令之后,我们可以看到断点生效了。
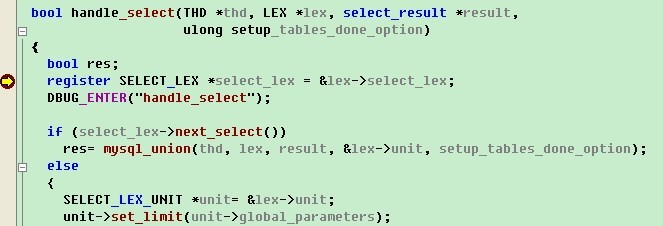
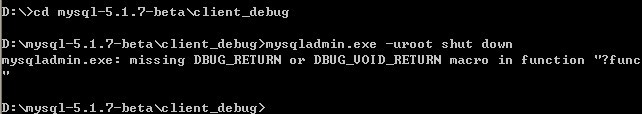
这样我们通过F10/F11/F5/shift+F11等常用的快捷键进行调试了。如果需要退出调试状态,则使用mysqladmin,如图(图中打印的一行错误信息不用理它,是系统的一个bug):
”
## 3)调试的技巧
Alex:“bingxi,这个我理解了,有没有一些常用的技巧。Alex常用的是通过快速监控,见下面的两图。
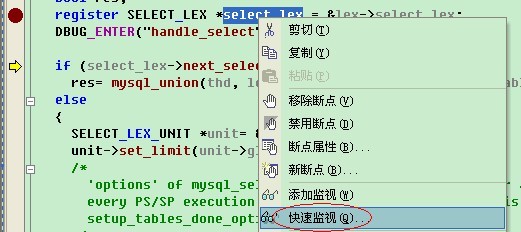
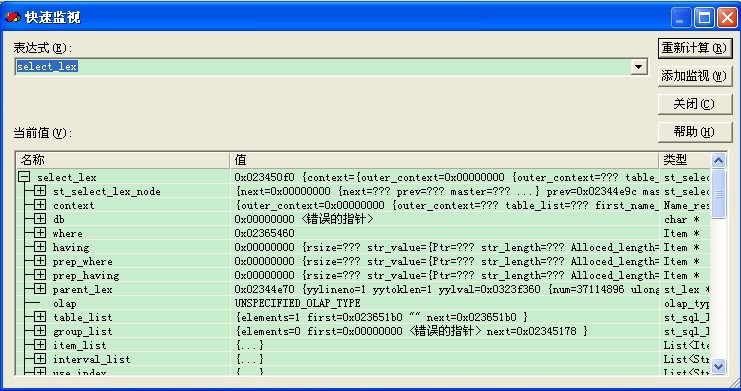
这样,我们可以看到变量的值。但是,遇到想测试函数,或者看宏的值就有点麻烦了。Bingxi,你给我讲讲。
”
Bingxi:“最常用的方法是直接分析算法,如果有些确实不太明白,可以通过自己写测试函数的方法进行调试。如果我想知道某一页属于哪个簇描述符,可以在fsp0fsp.c的文件尾加上我们自己的测试函数,同时设置断点:
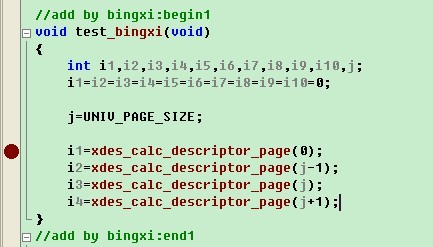
接着在该文件的文件头(添加内容为红色选中处),声明定义:
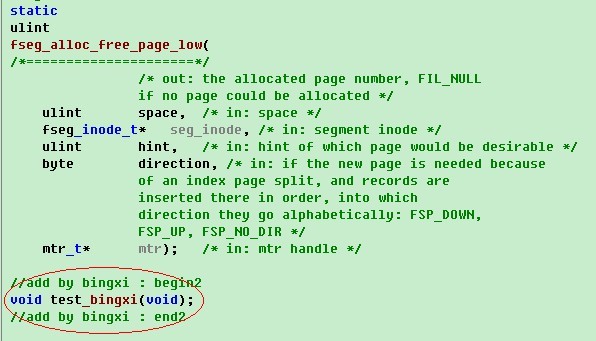
接着找一个函数,进行调用函数test_bingxi,这里我们选择fsp_get_space_header函数,因为这个函数在同一个文件,并且启动的时候会被执行。添加调用,添加内容为红色选中处。
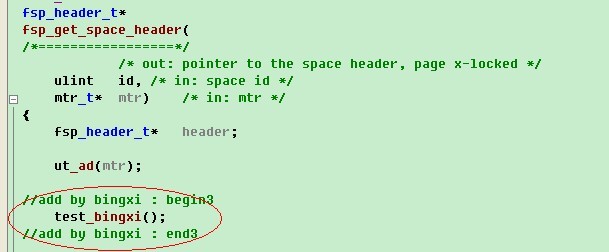
然后,我们启动调试,按F5进入断点。通过j值就可以知道UNIV_PAGE_SIZE的值,如果是多个宏计算后的值,也是一样的方法。通过i1值就可以知道xdes_calc_descriptor_page(0)的返回值。
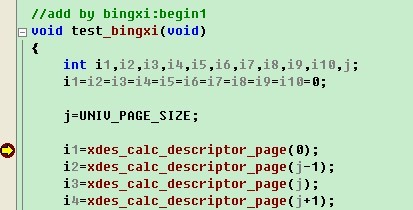
类似这样的方法,我们可以通过添加测试代码,将疑问的地方进行测试。今天调试的就说到这儿吧。
”
Alex:“ok,说完调试,开始正式进入innodb存储了。咱们也是初学者,需要多debug来解惑。今天不说晚安了,马上6点了,早安。”
Bingxi:“早安。”