8—innodb的list算法
最后更新于:2022-04-01 16:04:53
在上一篇里,bingxi和alex聊了下关于hash表的内容。在本篇里,会聊下关于list的内容。所谓list,就是双向链表,这样的算法在《数据结构》里面都是常见的。为了屏蔽差异性,类似于hash表,mysql将list通过宏来实现。
对应的文件为:
D:/mysql-5.1.7-beta/storage/innobase/include/ut0lst.h
## 1)常用结构体
Alex:“bingxi,考你一个问题:如果共享空间有4个文件,这四个文件是如何连在一起的。我们在ut0lst.h中看到了这样一段注释:
/* This module implements the two-way linear list which should be used
if a list is used in the database. Note that a single struct may belong
to two or more lists, provided that the list are given different names.
An example of the usage of the lists can be found in fil0fil.c. */
在注释中有提到fil0fil.c,那么我就问你共享空间的这个文件组织方式。
”
Bingxi:“要掌握这个具体怎么实现,我们还是需要进行调试。在调试之前,我们先从这段文字中看出几个有用的信息,然后再去验证它。1)这是一个双向链表,因此插入的时候有prev和next指针,2)一个结构体可能会属于多个list。
我们先来验证这两个信息。看fil_node_struct的定义,该结点属于两个list,一个对应的是文件list,另外一个是LURlist。
~~~
/* File node of a tablespace or the log data space */
struct fil_node_struct {
……
UT_LIST_NODE_T(fil_node_t) chain; //属于文件list
UT_LIST_NODE_T(fil_node_t) LRU; //属于LRUlist
……
};
~~~
我们再看一下UT_LIST_NODE_T的定义,如下:
~~~
#define UT_LIST_NODE_T(TYPE)/
struct {/
TYPE * prev; /* pointer to the previous node,/
NULL if start of list *//
TYPE * next; /* pointer to next node, NULL if end of list *//
}/
~~~
从这个定一个中,我们可以看到一个prev指针指向前一个结点,一个next指针指向下一个结点。
我们再来替代法来进行简化,将fil_node_struct中宏定义进行替代。替代后为:
~~~
typedef struct fil_node_struct fil_node_t;
/* File node of a tablespace or the log data space */
struct fil_node_struct {
……
struct {
fil_node_t * prev; /* pointer to the previous node,
NULL if start of list */
fil_node_t * next; /* pointer to next node, NULL if end of list */
}chain;
struct {
fil_node_t * prev; /* pointer to the previous node,
NULL if start of list */
fil_node_t * next; /* pointer to next node, NULL if end of list */
}LRU;
……
};
~~~
这样的,就好办了,取得chain的下一个结点,就是: (node->chain).next(其中fil_node_t* node)。
假设是共享表空间里面有4个文件,那么启动之后,链表是什么情况?
”
Alex:“ok,这个我们就来debug一下。debug之前我们要先看下,file_space_struct中的一个结构成员:chain。共享表空间对应的4个文件会挂在上面,然后每个file_node_t结构通过prev和next进行双向连接。
~~~
typedef struct fil_node_struct fil_node_t;
/* Tablespace or log data space: let us call them by a common name space */
struct fil_space_struct {
……
UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(fil_node_t) chain;
……
};
~~~
我们要看一下UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T的定义:
~~~
#define UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(TYPE)/
struct {/
ulintcount; /* count of nodes in list *//
TYPE * start; /* pointer to list start, NULL if empty *//
TYPE * end;/* pointer to list end, NULL if empty *//
}/
~~~
同样的,我们进行替换。会得到如下的情况:
~~~
typedef struct fil_node_struct fil_node_t;
/* Tablespace or log data space: let us call them by a common name space */
struct fil_space_struct {
……
struct {
ulintcount; /* count of nodes in list */
fil_node_t * start; /* pointer to list start, NULL if empty */
fil_node_t * end;/* pointer to list end, NULL if empty */
} chain;
……
};
~~~
从中我们得到第一个list成员,最后一个list成员,以及该list的成员数量。如果我们需要取得第一个成员就是:
fil_space_t* space;
fil_node_t* node;
……
node=(space->chain).start //这个已经通过宏来实
如果要取得再下一个,就是(node->chain).next(这个已经通过宏来实现)。
我们接着通过debug进行验证,配置my.ini(本例路径为D:/mysql-5.1.7-beta/my.ini,也可以存放在其它路径)。修改表空间,使用共享表空间为4个文件:
[mysqld]
innodb_data_file_path = ibdata1:10M;ibdata2:20M;ibdata3:30M;ibdata4:40M:autoextend
将D:/mysql-5.1.7-beta/data里面的内容恢复到初始化,所谓的初始化也就是将一开始代码解压缩时产生的原始data目录进行保存。需要初始化数据时,用该文件夹数据替代D:/mysql-5.1.7-beta/data的数据。
在fil_node_create函数设置断点,每执行一次看一次成员变量,等共享表空间对应的4个文件都执行之后我们可以看下该space对应的chain对应的取值。见图1:
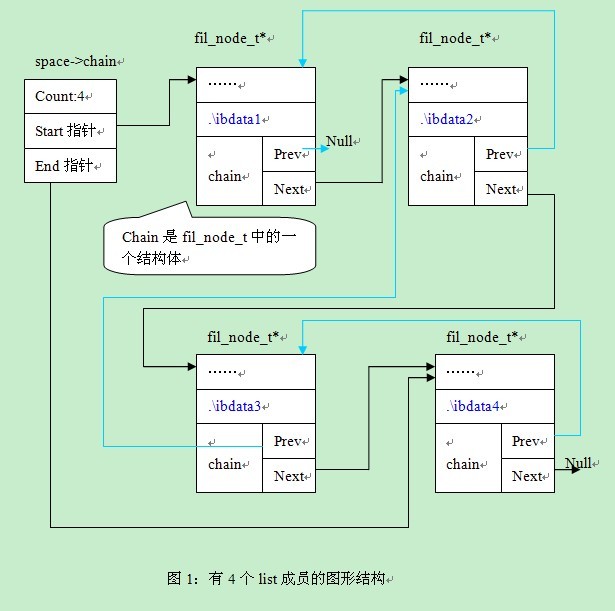
从图1中,我们可以看出4个结点通过prev及next指针相连,通过space->chain我们可以找到第一个结点,和最后一个结点。在图形中,通过天蓝色的线条表示prev。
通过这样的一个图形,我们会对list的表达方式有一个整体的了解。下面我们,在看一些具体函数的实现方式。
”
## 2)常用的函数
Bingxi:“好的,我们来看下插入函数吧。在图1中,我有一个疑问,问什么第一个成员的prev指向的是null,而不是指向space。”
Alex:“赞同,我们还是通过刚刚的例子来看下常用的插入函数UT_LIST_ADD_LAST,这个函数是往链表的末尾插入一个值。我们先看下该函数的定义,先不看其中的实现:
~~~
/***********************************************************************
Adds the node as the last element in a two-way linked list.
BASE has to be the base node (not a pointer to it). N has to be
the pointer to the node to be added to the list. NAME is the list name. */
#define UT_LIST_ADD_LAST(NAME, BASE, N)/
{/
ut_ad(N);/
((BASE).count)++;/
((N)->NAME).prev = (BASE).end;/
((N)->NAME).next = NULL;/
if ((BASE).end != NULL) {/
(((BASE).end)->NAME).next = (N);/
}/
(BASE).end = (N);/
if ((BASE).start == NULL) {/
(BASE).start = (N);/
}/
}/
~~~
插入文件结点的调用方式如下:
~~~
fil_node_t* node;
……
UT_LIST_ADD_LAST(chain, space->chain, node);
进行宏的替换,用下面的伪码表示:
fil_node_t* node;
void ut_list_add_last(chain, space->chain, node)
{
ut_ad(node); //断言语句
((space->chain).count)++; //步骤1:将列表的成员数量+1
//步骤2:设置插入结点的prev和next指针
//因为是插入到最后一个结点,所以next指针设置为null
//prev设置为插入前链表的最后一个结点,如果链表为空:(BASE).end为也为空,所以第一个结点成员的prev为空
((node)->chain).prev = (space->chain).end;
((node)->chain).next = NULL;/
//步骤3:如果插入链表结点不为空,则将node结点挂在已经结点的后面
if ((space->chain).end != NULL) {
(((space->chain).end)->chain).next = (node); //原来的最后一个结点的next指向新的结点
}
//步骤4:重新设置space->chain的end和start结点
//end结点很容易理解,就是指向新插入的结点,因为我们的操作就是插入到最后一个结点
//start的就要确认了:如果之前结点为空,则start也指向该结点,因为插入后只有一个结点,start和end都指向它
//如果start结点之前不为空,也就是链表有成员,将新成员插入到末尾的操作不影响start指针
(space->chain).end = (node);
if ((space->chain).start == NULL) {
(space->chain).start = (node);
}
}
~~~
”
Bingxi:“赞同你的看法,不过你少讲了一个内容,链表在创建的时候会进行初始化,
~~~
UT_LIST_INIT(space->chain); //函数调用
……
#define UT_LIST_INIT(BASE)/
{/
(BASE).count = 0;/
(BASE).start = NULL;/
(BASE).end = NULL;/
}/
~~~
将链表的count设置为0,start和end设置为null。另外,我发现alex最喜欢用代入法这样的傻方法,通过代入的方式来解释宏的实现,这也太傻了吧,哈哈。
”
Alex:“有时候,这样的方法也挺有效的,呵呵。第一次使用的时候可以用这样的方法先理解下,然后再看会简单些。我们现在直接看下类似的插入到链表首的宏的实现,这次我们直接看,不用代入法。
~~~
/***********************************************************************
Adds the node as the first element in a two-way linked list.
BASE has to be the base node (not a pointer to it). N has to be
the pointer to the node to be added to the list. NAME is the list name. */
#define UT_LIST_ADD_FIRST(NAME, BASE, N)/
{/
ut_ad(N);/
//步骤1:将列表的成员数量+1
((BASE).count)++;/
//步骤2,设置插入结点的prev和next指针
//因为是插入到首结点,所以该结点的prev为null
//新插入结点的next指向原链表的首结点
//这样就完成了新结点的prev和next指针的设置
((N)->NAME).next = (BASE).start;/
((N)->NAME).prev = NULL;/
//步骤3:如果插入前链表结点不为空,则原首结点的prev要进行重新设置
//将原首结点的prev指向新的结点
if ((BASE).start != NULL) {/
(((BASE).start)->NAME).prev = (N);/
}/
//步骤4:重新设置space->chain的end和start结点
//start指针很容易理解,因为我们是插入到链表首,所以该结点就是首结点
//同样的,如果插入前链表为空,也就是插入前end为空,则需要将end也指向这个唯一的链表成员
//如果插入前链表不为空,则不需要修改end指针。
(BASE).start = (N);/
if ((BASE).end == NULL) {/
(BASE).end = (N);/
}/
}/
~~~
另外有两个类似的宏,bingxi来看一下:UT_LIST_INSERT_AFTER、UT_LIST_REMOVE。
”
Bingxi:“这两个宏就不用看了吧,都是些链表的算法。留给大家自己看下吧。除了这两个宏之外,还有三个最基本的宏,用于获取base_node的三个成员:count、start、end。这里我把定义贴一下:
~~~
/************************************************************************
Alternative macro to get the number of nodes in a two-way list, i.e.,
its length. BASE is the base node (not a pointer to it). */
#define UT_LIST_GET_LEN(BASE)/
(BASE).count
/************************************************************************
Gets the first node in a two-way list, or returns NULL,
if the list is empty. BASE is the base node (not a pointer to it). */
#define UT_LIST_GET_FIRST(BASE)/
(BASE).start
/************************************************************************
Gets the last node in a two-way list, or returns NULL,
if the list is empty. BASE is the base node (not a pointer to it). */
#define UT_LIST_GET_LAST(BASE)/
(BASE).end
~~~
”
Alex:“嗯,这三个成员的比较简单。这一篇和上一篇,我们聊了两个基本算法结构,下一篇我们还会说一下动态数组。在第十篇写完之后,bingxi公布个list吧。将要开始写到innodb的文件存储内部格式,以及组织方法了。”
Bingxi:“好的,我回去想一下,第十篇出来后,就给你提供一个list,列出段、簇、页、记录等等的物理存储格式以及相互关系,然后按照list的组织方式来往下思考。”
Alex:“ok”