Python3 assert(断言)
最后更新于:2022-03-27 02:39:43
Python3 assert(断言)
Python assert(断言)用于判断一个表达式,在表达式条件为 false 的时候触发异常。
断言可以在条件不满足程序运行的情况下直接返回错误,而不必等待程序运行后出现崩溃的情况,例如我们的代码只能在 Linux 系统下运行,可以先判断当前系统是否符合条件。
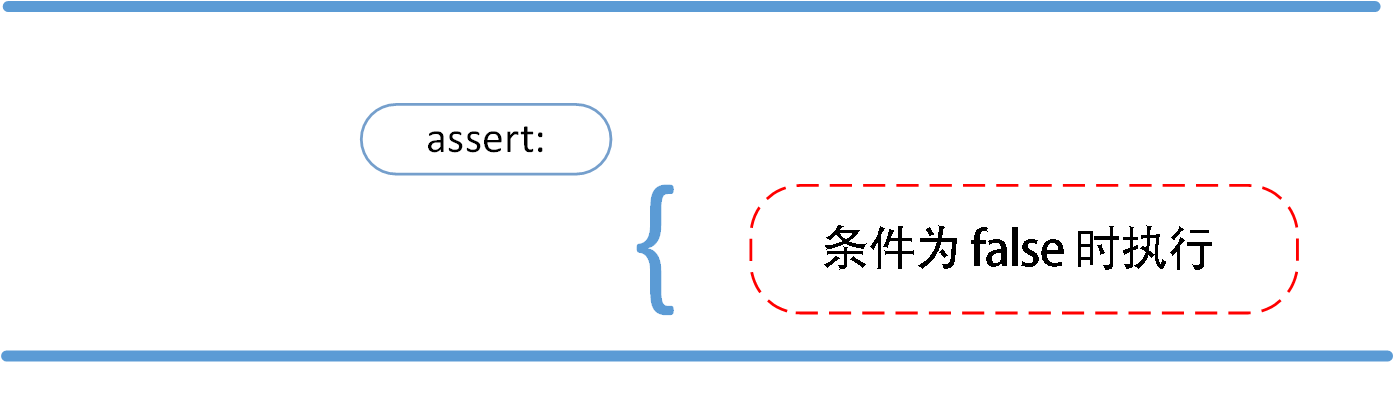
语法格式如下:
assert expression
等价于:
if not expression:
raise AssertionError
assert 后面也可以紧跟参数:
assert expression [, arguments]
等价于:
if not expression:
raise AssertionError(arguments)
以下为 assert 使用实例:
>>> assert True # 条件为 true 正常执行
>>> assert False # 条件为 false 触发异常
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AssertionError
>>> assert 1==1 # 条件为 true 正常执行
>>> assert 1==2 # 条件为 false 触发异常
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AssertionError
>>> assert False # 条件为 false 触发异常
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AssertionError
>>> assert 1==1 # 条件为 true 正常执行
>>> assert 1==2 # 条件为 false 触发异常
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AssertionError
>>> assert 1==2, ‘1 不等于 2’
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AssertionError: 1 不等于 2
>>>
以下实例判断当前系统是否为 Linux,如果不满足条件则直接触发异常,不必执行接下来的代码:
实例
import sys
assert (‘linux’ in sys.platform), "该代码只能在 Linux 下执行"
assert (‘linux’ in sys.platform), "该代码只能在 Linux 下执行"
# 接下来要执行的代码
 Python3 错误和异常
Python3 错误和异常