OpenCV2学习笔记(十九)
最后更新于:2022-04-01 06:36:28
##Kalman滤波算法
在视频跟踪处理中,预测目标运动轨迹是一项基本任务。目标运动状态估计的目的有三个:一是对目标过去的状态进行平滑;二是对目标现在的运动状态进行滤波;三是对目标未来的运动状态进行预测。物体的运动状态一般包括目标位置、速度、加速度等。著名的Kalman滤波技术就是其中一种,这是一种线性系统估计技术。
OpenCV中自带了kalman滤波的代码和例程,可参照kalman.cpp,它存在于类KalmanFilter中。kalman滤波算法的调用比较方便,主要的难点是了解多个参数和矩阵计算公式。一个总体的思路是,需要了解前一时刻的状态估计值x和当前的观测值y,然后建立状态方程和观测方程。经过一些运算后即可预测下一步的状态。
**一、离散时间线性动态系统的状态方程**
Kalman滤波利用线性系统状态方程,通过系统输入输出观测数据,对系统状态进行最优估计的算法。由于观测数据中包括系统中的噪声和干扰的影响,所以最优估计也可看作是滤波过程。一个**线性系统**是采用状态方程、观测方程及其初始条件来描述。线性离散时间系统的一般状态方程可描述为:
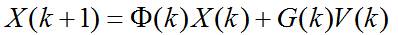
其中, 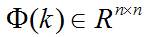是状态转移矩阵, 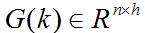是过程噪声增益矩阵。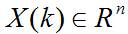是k时刻目标的状态向量, 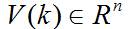是过程噪声,它是具有均值为零、方差矩阵为Q(k)的高斯噪声向量,即:
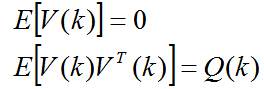
**二、传感器的观测方程**
传感器的通用观测方程为:
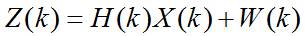
这里, 是传感器在 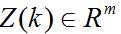时刻的观测向量,观测噪声 是具有零均值和正定协方差矩阵R(k)的高斯分布测量噪声向量,即:
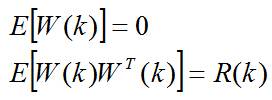
**三、初始状态的描述**
初始状态 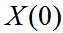是高斯的,具有均值 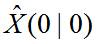和协方差 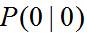,即:
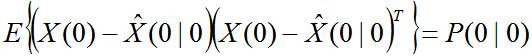
以上的描述比较抽象,因此记录一个例子加以说明:
例:目标沿x轴作匀速直线运动,过程噪声为速度噪声,试写出目标的状态方程。
解:由题意知,目标的状态为:
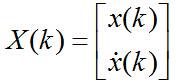
用T表示时间间隔,ux表速度噪声,则有:
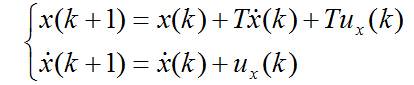
写成矩阵形式为:
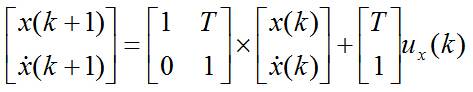
令:
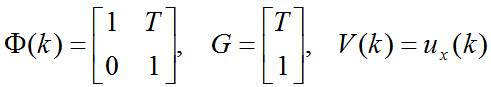
则有:
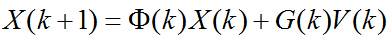
其中:
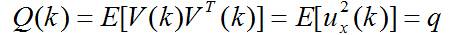
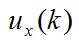为均值等于0,方差为q的高斯噪声。
在OpenCV中自带的例程里面描述了一个一维的运动跟踪,该点在一个圆弧上运动,只有一个自由度即角度。因此只需建立匀速运动模型即可。
例程的路径:C:\opencv\sources\samples\cpp\kalman.cpp
~~~
在代码中各变量的对应情况如下:
状态估计值X对应:state
当前观测值Z对应:measurement
KalmanFilter类内成员变量transitionMatrix即为状态转移方程中的矩阵A
KalmanFilter类内成员变量measurementMatrix即为量测方程中矩阵C
Mat statePre; //!< predicted state (x'(k)): x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
Mat statePost; //!< corrected state (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
Mat transitionMatrix; //!< state transition matrix (A)
Mat controlMatrix; //!< control matrix (B) (not used if there is no control)
Mat measurementMatrix; //!< measurement matrix (H)
Mat processNoiseCov; //!< process noise covariance matrix (Q)
Mat measurementNoiseCov;//!< measurement noise covariance matrix (R)
Mat errorCovPre; //!< priori error estimate covariance matrix (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)*/
Mat gain; //!< Kalman gain matrix (K(k)): K(k)=P'(k)*Ht*inv(H*P'(k)*Ht+R)
Mat errorCovPost; //!< posteriori error estimate covariance matrix (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
~~~
以下是OpenCV/modules/video/src/Kalman.cpp的源代码,后续需继续分析这些代码:
~~~
/*M///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// IMPORTANT: READ BEFORE DOWNLOADING, COPYING, INSTALLING OR USING.
//
// By downloading, copying, installing or using the software you agree to this license.
// If you do not agree to this license, do not download, install,
// copy or use the software.
//
//
// Intel License Agreement
// For Open Source Computer Vision Library
//
// Copyright (C) 2000, Intel Corporation, all rights reserved.
// Third party copyrights are property of their respective owners.
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
// are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
//
// * Redistribution's of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
// this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
//
// * Redistribution's in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
// this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
// and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
//
// * The name of Intel Corporation may not be used to endorse or promote products
// derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// This software is provided by the copyright holders and contributors "as is" and
// any express or implied warranties, including, but not limited to, the implied
// warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose are disclaimed.
// In no event shall the Intel Corporation or contributors be liable for any direct,
// indirect, incidental, special, exemplary, or consequential damages
// (including, but not limited to, procurement of substitute goods or services;
// loss of use, data, or profits; or business interruption) however caused
// and on any theory of liability, whether in contract, strict liability,
// or tort (including negligence or otherwise) arising in any way out of
// the use of this software, even if advised of the possibility of such damage.
//
//M*/
#include "precomp.hpp"
CV_IMPL CvKalman*
cvCreateKalman( int DP, int MP, int CP )
{
CvKalman *kalman = 0;
if( DP <= 0 || MP <= 0 )
CV_Error( CV_StsOutOfRange,
"state and measurement vectors must have positive number of dimensions" );
if( CP < 0 )
CP = DP;
/* allocating memory for the structure */
kalman = (CvKalman *)cvAlloc( sizeof( CvKalman ));
memset( kalman, 0, sizeof(*kalman));
kalman->DP = DP;
kalman->MP = MP;
kalman->CP = CP;
kalman->state_pre = cvCreateMat( DP, 1, CV_32FC1 );
cvZero( kalman->state_pre );
kalman->state_post = cvCreateMat( DP, 1, CV_32FC1 );
cvZero( kalman->state_post );
kalman->transition_matrix = cvCreateMat( DP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
cvSetIdentity( kalman->transition_matrix );
kalman->process_noise_cov = cvCreateMat( DP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
cvSetIdentity( kalman->process_noise_cov );
kalman->measurement_matrix = cvCreateMat( MP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
cvZero( kalman->measurement_matrix );
kalman->measurement_noise_cov = cvCreateMat( MP, MP, CV_32FC1 );
cvSetIdentity( kalman->measurement_noise_cov );
kalman->error_cov_pre = cvCreateMat( DP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
kalman->error_cov_post = cvCreateMat( DP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
cvZero( kalman->error_cov_post );
kalman->gain = cvCreateMat( DP, MP, CV_32FC1 );
if( CP > 0 )
{
kalman->control_matrix = cvCreateMat( DP, CP, CV_32FC1 );
cvZero( kalman->control_matrix );
}
kalman->temp1 = cvCreateMat( DP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
kalman->temp2 = cvCreateMat( MP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
kalman->temp3 = cvCreateMat( MP, MP, CV_32FC1 );
kalman->temp4 = cvCreateMat( MP, DP, CV_32FC1 );
kalman->temp5 = cvCreateMat( MP, 1, CV_32FC1 );
#if 1
kalman->PosterState = kalman->state_pre->data.fl;
kalman->PriorState = kalman->state_post->data.fl;
kalman->DynamMatr = kalman->transition_matrix->data.fl;
kalman->MeasurementMatr = kalman->measurement_matrix->data.fl;
kalman->MNCovariance = kalman->measurement_noise_cov->data.fl;
kalman->PNCovariance = kalman->process_noise_cov->data.fl;
kalman->KalmGainMatr = kalman->gain->data.fl;
kalman->PriorErrorCovariance = kalman->error_cov_pre->data.fl;
kalman->PosterErrorCovariance = kalman->error_cov_post->data.fl;
#endif
return kalman;
}
CV_IMPL void
cvReleaseKalman( CvKalman** _kalman )
{
CvKalman *kalman;
if( !_kalman )
CV_Error( CV_StsNullPtr, "" );
kalman = *_kalman;
if( !kalman )
return;
/* freeing the memory */
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->state_pre );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->state_post );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->transition_matrix );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->control_matrix );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->measurement_matrix );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->process_noise_cov );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->measurement_noise_cov );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->error_cov_pre );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->gain );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->error_cov_post );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->temp1 );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->temp2 );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->temp3 );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->temp4 );
cvReleaseMat( &kalman->temp5 );
memset( kalman, 0, sizeof(*kalman));
/* deallocating the structure */
cvFree( _kalman );
}
CV_IMPL const CvMat*
cvKalmanPredict( CvKalman* kalman, const CvMat* control )
{
if( !kalman )
CV_Error( CV_StsNullPtr, "" );
/* update the state */
/* x'(k) = A*x(k) */
cvMatMulAdd( kalman->transition_matrix, kalman->state_post, 0, kalman->state_pre );
if( control && kalman->CP > 0 )
/* x'(k) = x'(k) + B*u(k) */
cvMatMulAdd( kalman->control_matrix, control, kalman->state_pre, kalman->state_pre );
/* update error covariance matrices */
/* temp1 = A*P(k) */
cvMatMulAdd( kalman->transition_matrix, kalman->error_cov_post, 0, kalman->temp1 );
/* P'(k) = temp1*At + Q */
cvGEMM( kalman->temp1, kalman->transition_matrix, 1, kalman->process_noise_cov, 1,
kalman->error_cov_pre, CV_GEMM_B_T );
/* handle the case when there will be measurement before the next predict */
cvCopy(kalman->state_pre, kalman->state_post);
return kalman->state_pre;
}
CV_IMPL const CvMat*
cvKalmanCorrect( CvKalman* kalman, const CvMat* measurement )
{
if( !kalman || !measurement )
CV_Error( CV_StsNullPtr, "" );
/* temp2 = H*P'(k) */
cvMatMulAdd( kalman->measurement_matrix, kalman->error_cov_pre, 0, kalman->temp2 );
/* temp3 = temp2*Ht + R */
cvGEMM( kalman->temp2, kalman->measurement_matrix, 1,
kalman->measurement_noise_cov, 1, kalman->temp3, CV_GEMM_B_T );
/* temp4 = inv(temp3)*temp2 = Kt(k) */
cvSolve( kalman->temp3, kalman->temp2, kalman->temp4, CV_SVD );
/* K(k) */
cvTranspose( kalman->temp4, kalman->gain );
/* temp5 = z(k) - H*x'(k) */
cvGEMM( kalman->measurement_matrix, kalman->state_pre, -1, measurement, 1, kalman->temp5 );
/* x(k) = x'(k) + K(k)*temp5 */
cvMatMulAdd( kalman->gain, kalman->temp5, kalman->state_pre, kalman->state_post );
/* P(k) = P'(k) - K(k)*temp2 */
cvGEMM( kalman->gain, kalman->temp2, -1, kalman->error_cov_pre, 1,
kalman->error_cov_post, 0 );
return kalman->state_post;
}
namespace cv
{
KalmanFilter::KalmanFilter() {}
KalmanFilter::KalmanFilter(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams, int type)
{
init(dynamParams, measureParams, controlParams, type);
}
void KalmanFilter::init(int DP, int MP, int CP, int type)
{
CV_Assert( DP > 0 && MP > 0 );
CV_Assert( type == CV_32F || type == CV_64F );
CP = std::max(CP, 0);
statePre = Mat::zeros(DP, 1, type);
statePost = Mat::zeros(DP, 1, type);
transitionMatrix = Mat::eye(DP, DP, type);
processNoiseCov = Mat::eye(DP, DP, type);
measurementMatrix = Mat::zeros(MP, DP, type);
measurementNoiseCov = Mat::eye(MP, MP, type);
errorCovPre = Mat::zeros(DP, DP, type);
errorCovPost = Mat::zeros(DP, DP, type);
gain = Mat::zeros(DP, MP, type);
if( CP > 0 )
controlMatrix = Mat::zeros(DP, CP, type);
else
controlMatrix.release();
temp1.create(DP, DP, type);
temp2.create(MP, DP, type);
temp3.create(MP, MP, type);
temp4.create(MP, DP, type);
temp5.create(MP, 1, type);
}
const Mat& KalmanFilter::predict(const Mat& control)
{
// update the state: x'(k) = A*x(k)
statePre = transitionMatrix*statePost;
if( control.data )
// x'(k) = x'(k) + B*u(k)
statePre += controlMatrix*control;
// update error covariance matrices: temp1 = A*P(k)
temp1 = transitionMatrix*errorCovPost;
// P'(k) = temp1*At + Q
gemm(temp1, transitionMatrix, 1, processNoiseCov, 1, errorCovPre, GEMM_2_T);
// handle the case when there will be measurement before the next predict.
statePre.copyTo(statePost);
errorCovPre.copyTo(errorCovPost);
return statePre;
}
const Mat& KalmanFilter::correct(const Mat& measurement)
{
// temp2 = H*P'(k)
temp2 = measurementMatrix * errorCovPre;
// temp3 = temp2*Ht + R
gemm(temp2, measurementMatrix, 1, measurementNoiseCov, 1, temp3, GEMM_2_T);
// temp4 = inv(temp3)*temp2 = Kt(k)
solve(temp3, temp2, temp4, DECOMP_SVD);
// K(k)
gain = temp4.t();
// temp5 = z(k) - H*x'(k)
temp5 = measurement - measurementMatrix*statePre;
// x(k) = x'(k) + K(k)*temp5
statePost = statePre + gain*temp5;
// P(k) = P'(k) - K(k)*temp2
errorCovPost = errorCovPre - gain*temp2;
return statePost;
}
}
~~~
参考链接:[http://blog.csdn.net/yang_xian521/article/details/7050398](http://blog.csdn.net/yang_xian521/article/details/7050398)